16. Advanced Methods¶
Todo
Write short introduction
16.1. Creating bonds when particles collide¶
Please cite [ALK+ed] when using dynamic bonding.
With the help of this feature, bonds between particles can be created automatically during the simulation, every time two particles collide. This is useful for simulations of chemical reactions and irreversible adhesion processes. Both, sliding and non-sliding contacts can be created.
The collision detection is controlled via the espressomd.system.System.collision_detection attribute, which is an instance of the class espressomd.collision_detection.CollisionDetection.
Several modes are available for different types of binding.
"bind_centers": adds a pair-bond between two particles at their first collision. By making the bonded interaction stiff enough, the particles can be held together after the collision. Note that the particles can still slide on each others’ surface, as the pair bond is not directional. This mode is set up as follows:import espressomd from espressomd.interactions import HarmonicBond system = espressomd.System() bond_centers = HarmonicBond(k=1000, r_0=<CUTOFF>) system.bonded_inter.add(bond_centers) system.collision_detection.set_params(mode="bind_centers", distance=<CUTOFF>, bond_centers=bond_centers)
The parameters are as follows:
distanceis the distance between two particles at which the binding is triggered. This cutoff distance,<CUTOFF>in the example above, is typically chosen slightly larger than the particle diameter. It is also a good choice for the equilibrium length of the bond.bond_centersis the bonded interaction (an instance ofespressomd.interactions.HarmonicBond) to be created between the particles. No guarantees are made regarding which of the two colliding particles gets the bond. Once there is a bond of this type on any of the colliding particles, no further binding occurs for this pair of particles.
"bind_at_point_of_collision": this mode prevents sliding of the colliding particles at the contact. This is achieved by creating two virtual sites at the point of collision. They are rigidly connected to the colliding particles, respectively. A bond is then created between the virtual sites, or an angular bond between the two colliding particles and the virtual particles. In the latter case, the virtual particles are the centers of the angle potentials (particle 2 in the description of the angle potential (see Bond-angle interactions). Due to the rigid connection between each of the particles in the collision and its respective virtual site, a sliding at the contact point is no longer possible. See the documentation on Rigid arrangements of particles for details. In addition to the bond between the virtual sites, the bond between the colliding particles is also created, i.e., the"bind_at_point_of_collision"mode implicitly includes the"bind_centers"mode. You can either use a real bonded interaction to prevent wobbling around the point of contact or you can useespressomd.interactions.Virtualwhich acts as a marker, only. The method is setup as follows:system.collision_detection.set_params(mode="bind_at_point_of_collision", distance=<CUTOFF>, bond_centers=<BOND_CENTERS>, bond_vs=<BOND_VS>, part_type_vs=<PART_TYPE_VS>, vs_placement=<VS_PLACEMENT>)
The parameters
distanceandbond_centershave the same meaning as in the"bind_centers"mode. The remaining parameters are as follows:bond_vsis the bond to be added between the two virtual sites created on collision. This is either a pair-bond with an equilibrium length matching the distance between the virtual sites, or an angle bond fully stretched in its equilibrium configuration.part_type_vsis the particle type assigned to the virtual sites created on collision. In nearly all cases, no non-bonded interactions should be defined for this particle type.vs_placementcontrols, where on the line connecting the centers of the colliding particles, the virtual sites are placed. A value of 0 means that the virtual sites are placed at the same position as the colliding particles on which they are based. A value of 0.5 will result in the virtual sites being placed ad the mid-point between the two colliding particles. A value of 1 will result the virtual site associated to the first colliding particle to be placed at the position of the second colliding particle. In most cases, 0.5, is a good choice. Then, the bond connecting the virtual sites should have an equilibrium length of zero.
"glue_to_surface": This mode is used to irreversibly attach small particles to the surface of a big particle. It is asymmetric in that several small particles can be bound to a big particle but not vice versa. The small particles can change type after collision to make them inert. On collision, a single virtual site is placed and related to the big particle. Then, a bond (bond_centers) connects the big and the small particle. A second bond (bond_vs) connects the virtual site and the small particle. Further required parameters are:part_type_to_attach_vs_to: Type of the particle to which the virtual site is attached, i.e., the big particle.part_type_to_be_glued: Type of the particle bound to the virtual site (the small particle).part_type_after_glueing: The type assigned to the particle bound to the virtual site (small particle) after the collision.part_type_vs: Particle type assigned to the virtual site created during the collision.distance_glued_particle_to_vs: Distance of the virtual site to the particle being bound to it (small particle).
Note: When the type of a particle is changed on collision, this makes the particle inert with regards to further collision. Should a particle of type
part_type_to_be_gluedcollide with two particles in a single time step, no guarantees are made with regards to which partner is selected. In particular, there is no guarantee that the choice is unbiased.
"bind_three_particles"allows for the creation of agglomerates which maintain their shape similarly to those create by the mode"bind_at_point_of_collision". The present approach works without virtual sites. Instead, for each two-particle collision, the surrounding is searched for a third particle. If one is found, angular bonds are placed to maintain the local shape. If all three particles are within the cutoff distance, an angle bond is added on each of the three particles in addition to the distance based bonds between the particle centers. If two particles are within the cutoff of a central particle (e.g., chain of three particles) an angle bond is placed on the central particle. The angular bonds being added are determined from the angle between the particles. This method does not depend on the particles’ rotational degrees of freedom being integrated. Virtual sites are also not required. The method, along with the corresponding bonds are setup as follows:n_angle_bonds = 181 # 0 to 180 degrees in one degree steps for i in range(0, res, 1): self.s.bonded_inter[i] = Angle_Harmonic( bend=1, phi0=float(i) / (res - 1) * np.pi) # Create the bond passed to bond_centers here and add it to the system self.s.collision_detection.set_params(mode="bind_three_particles", bond_centers=<BOND_CENTERS>, bond_three_particles=0, three_particle_binding_angle_resolution=res, distance=<CUTOFF>)
Important: The bonds for the angles are mapped via their numerical bond ids. In this example, ids from 0 to 180 are used. All other bonds required for the simulation need to be added to the system after those bonds. In particular, this applies to the bonded interaction passed via
bond_centers
The following limitations currently apply for the collision detection:
- No distinction is currently made between different particle types for the
"bind_centers"method. - The
"bind at point of collision"and"glue to surface"approaches require the featureVIRTUAL_SITES_RELATIVEto be activated inmyconfig.hpp. - The
"bind at point of collision"approach cannot handle collisions between virtual sites
16.2. Swimmer Reactions¶
With the help of the feature SWIMMER_REACTIONS, one can define three particle types to act as reactant (e.g. \(\mathrm{H_2 O_2}\)), catalyzer (e.g. platinum), and product (e.g. \(\mathrm{O_2}\) and \(\mathrm{H_2 O}\)). The current setup allows one to simulate active swimmers and their chemical propulsion.
For a Janus swimmer consisting of platinum on one hemisphere and gold on the other hemisphere, both surfaces catalytically induce a reaction. We assume an initial abundance of hydrogen peroxide and absence of products, so that back (recombination) reactions seldom occur at the surface. A typical model for the propulsion of such a particle assumes
That is, catalytic surfaces induce a reactions that produce charged species by consuming hydrogen peroxide. It is the change in distribution of charged species that leads to motion of the swimmer, a process referred to as self-electrophoresis. A minimal model for this would be
where on the upper half of the catalyst \(C^{+}\) a species \(A\) is converted into \(B\), and on the lower half \(C^{-}\) the opposite reaction takes place. Note that when \(A\) and \(B\) are charged, this reaction conserves charge, provided the rates are equal. Note that this feature uses the word catalyst in a meaning which cannot be brought into agreement with the definition of a catalyst. If the catalyst \(C^{+}\) catalyzes (on average) the reaction, where \(A\) is converted to \(B\), then it is impossible that a catalyst \(C^{-}\) performs (on average) the reverse reaction. For the example with hydrogen peroxide this would mean that hydrogen peroxide is created spontaneously using a catalyst (under the same environment where another catalyst wants to split hydrogen peroxide). This is chemically impossible. What is meant to be modeled is that hydrogen peroxide is constantly flowing into the system from the bulk and therefore it is not depleted. This behaviour cannot be modeled using a catalyst (in the defined meaning of the word catalyst).
In ESPResSo the orientation of a catalyzer particle is used to define hemispheres; half spaces going through the particle’s center. The reaction region is bounded by the reaction range: \(r\). Inside the reaction range, we react only reactant-product pairs. The particles in a pair are swapped from hemisphere to another with a rate prescribed by
with the reaction rate \(k_{\mathrm{ct}}\) and the simulation time step \(\Delta t\). A pair may be swapped only once per MD time step, to avoid a no-net-effect situation. That is, we allow an exchange move only when the following conditions are met:
- Both partners of the reactant-product pair have to reside within the reaction range.
- The product has to reside in the upper half-space of the reaction range.
- The reactant has to reside in the lower half-space of the reaction range.
Self-propulsion is achieved by imposing an interaction asymmetry between the partners of a swapped pair. That is, the heterogeneous distribution of chemical species induced by the swapping leads to a net force on the particle, counter balanced by friction.
To set up the system for catalytic reactions the class espressomd.reaction.Reaction
can be used.
from espressomd.reaction import Reaction
system = espressomd.System()
# setting up particles etc
r = Reaction(product_type=1, reactant_type=2, catalyzer_type=0,
ct_range=2, ct_rate=0.2, eq_rate=0)
r.start()
r.stop()
print r
- the first invocation of
Reaction, in the above example, defines a reaction with particles of type number 2 as reactant, type 0 as catalyzer and type 1 as product [3]. The catalytic reaction rate constant is given by \(\mathrm{ct\_rate}\) [4] and to override the default rate constant for the equilibrium reaction ( = 0), one can specify it by aseq_rata. By default each reactant particle is checked against each catalyst particle (react_once=False). However, when creating smooth surfaces using many catalyst particles, it can be desirable to let the reaction rate be independent of the surface density of these particles. That is, each particle has a likelihood of reacting in the vicinity of the surface (distance is less than \(r\)) as specified by the rate constant, i.e., not according to \(P_{\text{cvt}} = 1 - \exp \left( - n k\Delta t \right)\), with \(n\) the number of local catalysts. To accomplish this, each reactant is considered only once each time step by using the optionreact_once=True. The reaction command is set up such that the different properties may be influenced individually. r.stop()disables the reaction. Note that at the moment, there can only be one reaction in the simulation.print rreturns the current reaction parameters.
In future versions of ESPResSo the capabilities of the SWIMMER_REACTIONS feature may be generalized
to handle multiple reactant, catalyzer, and product types, as well as
more general reaction schemes. Other changes may involve merging the
current implementation with the COLLISION_DETECTION feature.
Footnotes
| [3] | Only one type of particle can be assigned to each of these three reaction species and no particle type may be assigned to multiple species. That is, currently does not support particles of type 1 and 2 both to be reactants, nor can particles of type 1 be a reactant as well as a catalyst. Moreover, only one of these reactions can be implemented in a single Tcl script. If, for instance, there is a reaction involving particle types 1, 2, and 4, there cannot be a second reaction involving particles of type 5, 6, and 8. It is however possible to modify the reaction properties for a given set of types during the simulation. |
| [4] | Currently only strictly positive values of the catalytic conversion
rate constant are allowed. Setting the value to zero is equivalent to
r.stop(). |
16.3. Lees-Edwards boundary conditions¶
Lees-Edwards boundary conditions are not available in the current version of ESPResSo.
16.4. Immersed Boundary Method for soft elastic objects¶
Please contact the Biofluid Simulation and Modeling Group at the University of Bayreuth if you plan to use this feature.
With the Immersed Boundary Method (IBM), soft particles are considered as an infinitely thin shell filled with liquid (see e.g. [Pes03][CF10][Kruger11]). When the shell is deformed by an external flow, it responds with elastic restoring forces which are transmitted into the fluid. In the present case, the inner and outer liquid are of the same type and are simulated using lattice Boltzmann.
Numerically, the shell is discretized by a set of marker points
connected by triangles. The marker points are advected with exactly
the local fluid velocity, i.e., they do not possess a mass nor a
friction coefficient (this is different from the Object-in-Fluid method
below). We implement these marker points as virtual tracer
particles which are not integrated using the usual velocity-Verlet
scheme, but instead are propagated using a simple Euler algorithm with
the local fluid velocity (if the IMMERSED_BOUNDARY feature is turned
on).
The immersed boundary method consists of two components, which can be used independently:
- Inertialess lattice Boltzmann tracers implemented as virtual sites
- Interactions providing the elastic forces for the particles forming the surface. These are described below.
To compute the elastic forces, three new bonded interactions are defined: espressomd.interactions.IBM_Triel, espressomd.interactions.IBM_Tribend and espressomd.interactions.IBM_VolCons.
espressomd.interactions.IBM_Triel is used to compute elastic shear forces. To setup an interaction, use:
tri1 = IBM_Triel(ind1=0, ind2=1, ind3=2, elasticLaw="Skalak", k1=0.1, k2=0, maxDist=2.4)
where ind1, ind2 and ind3 represent the indices of the three marker points making up the triangle. The parameter maxDist
specifies the maximum stretch above which the bond is considered broken. The parameter elasticLaw can be either "NeoHookean" or "Skalak".
The parameters k1 and k2 are the elastic moduli.
espressomd.interactions.IBM_Tribend computes out-of-plane bending forces. To setup an interaction, use:
tribend = IBM_Tribend(ind1=0, ind2=1, ind3=2, ind4=3, kb=1, refShape="Initial")
where ind1, ind2, ind3 and ind4 are four marker points corresponding to two neighboring triangles. The indices ind1 and ind3 contain the shared edge. Note that the marker points within a triangle must be labelled such that the normal vector \(\vec{n} = (\vec{r}_\text{ind2} - \vec{r}_\text{ind1}) \times (\vec{r}_\text{ind3} - \vec{r}_\text{ind1})\) points outward of the elastic object.
The reference (zero energy) shape can be either "Flat" or the initial curvature "Initial".
The bending modulus is kb.
espressomd.interactions.IBM_VolCons is a volume-conservation force. Without this correction, the volume of the soft object tends to shrink over time due to numerical inaccuracies. Therefore, this implements an artificial force intended to keep the volume constant. If volume conservation is to be used for a given soft particle, the interaction must be added to every marker point belonging to that object.
volCons = IBM_VolCons(softID=1, kappaV=kV)
where softID identifies the soft particle and kv is a volumetric spring constant.
Note that the espressomd.interactions.IBM_VolCons bond does not need a bond partner. It is added to a particle as follows:
s.part[0].add_bond((Volcons,))
The comma is needed to force Python to create a tuple containing a single item.
For a more detailed description, see e.g. Guckenberger and Gekle, J. Phys. Cond. Mat. (2017) or contact us. This feature probably does not work with advanced LB features such electro kinetics or Shan-Chen.
A sample script is provided in the samples/immersed_boundary directory of the source distribution.
16.5. Object-in-fluid¶
If you plan to use this feature, please contact the Cell-in-fluid Research Group at the University of Zilina:
If using this module, please cite [CimrakGJanvcigova14] (Bibtex key Cimrak2014 in doc/sphinx/zref.bib) and [CimrakGS12] (Bibtex key Cimrak2012 in doc/sphinx/zref.bib)
16.5.1. Triangulations of elastic objects¶
some_nodes.dat should contain triplets of floats (one
triplet per line), where each triplet represents the \(x, y\) and
\(z\) coordinates of one node of the surface triangulation. No
additional information should be written in this file, so this means
that the number of lines equals to the number of surface nodes. The
coordinates of the nodes should be specified in such a way that the
approximate center of mass of the object corresponds to the origin
(0,0,0). This is for convenience when placing the objects at desired
locations later.some_triangles.dat should also contain triplets of
numbers, this time integers. These integers refer to the IDs of the nodes in
the some_nodes.dat file and specify which three nodes form a
triangle. Please, note that the nodes’ IDs start at 0, i.e.
the node written in the first line of some_nodes.dat has ID 0, the
node in the second line, has ID 1, etc.16.5.2. Description of sample script¶
Note
The following features are required:
LB, LB_BOUNDARIES,
EXTERNAL_FORCES,
MASS, CONSTRAINTS, OIF_LOCAL_FORCES,
OIF_GLOBAL_FORCES, SOFT_SPHERE, MEMBRANE_COLLISION
The script described in this section is available in samples/object-in-fluid/two-cells.py and also at
http://cell-in-fluid.kst.fri.uniza.sk/en/content/oif-espresso.
In the first few lines, the script includes several imports related to the red blood cell model, fluid, boundaries and interactions. Then we have:
system = espressomd.System(box_l=(22, 14, 15))
system.time_step = 0.1
system.cell_system.skin = 0.2
Here we set up a system and its most important parameters. The skin
depth tunes the system’s performance. The one important thing a user needs to know
about it is that it has to be strictly less than half the grid size.
box_l sets up the dimensions of the 3D simulation box. You might
wonder what the units are. For now, you can think of them as
micrometers, we will return to them later.
time_step is the time step that will be used in the simulation, for
the purposes here, in microseconds. It allows separate specification of
time step for the particles and for the fluid. This is useful when one
takes into account also thermal fluctuations relevant on molecular
level, however, for us, both of these time steps will mostly be
identical.
16.5.2.1. Specification of immersed objects¶
cell_type = OifCellType(nodesfile="input/rbc374nodes.dat",
trianglesfile="input/rbc374triangles.dat", system=system,
ks=0.02, kb=0.016, kal=0.02, kag=0.9, kv=0.5, resize=[2.0, 2.0, 2.0])
We do not create elastic objects directly but rather each one has to
correspond to a template, cell_type, that has been created first.
The advantage of this approach is clear when creating many objects of
the same type that only differ by e.g. position or rotation, because in
such case it significantly speeds up the creation of objects that are
just copies of the same template.
The three mandatory arguments are nodes-file and triangles-file
that specify input data files with desired triangulation and system
that specifies the ESPResSo system. The relaxed mesh triangles should be
as close to equilateral as possible with average edge length
approximately equal to the space discretisation step \(\Delta x\).
While these lengths vary during the simulation, the connectivity of the
mesh nodes never changes. Basic meshes can be downloaded from our
website. This script assumes that the two necessary files are located
inside an input directory that resides in the same folder as the
simulation script.
All other arguments are optional. resize defines resizing in the
\(x, y, z\) directions with respect to unit size of the object, so
in this case, the cell radius will be 2. ks, kb, kal,
kag, kv specify the elastic properties: stretching, bending,
local area conservation, global area conservation and volume
conservation respectively.
The backslash allows the long command to continue over multiple lines.
cell = OifCell(cellType=cell_type, partType=0, origin=[5.0, 5.0, 3.0])
Next, an actual object is created and its initial position is saved to a
.vtk file (the directory output/sim1 needs to exist before the
script is executed). Each object has to have a unique ID, specified using the
keyword partType. The IDs have to start at 0 and increase
consecutively. The other two mandatory arguments are cellType and
origin. cellType specifies which previously defined cell type
will be used for this object. origin gives placement of object’s
center in the simulation box.
16.5.2.2. Specification of fluid and movement¶
lbf = espressomd.lb.LBFluid(agrid=1, dens=1.0, visc=1.5, fric=1.5,
tau=time_step, ext_force_density=[0.002, 0.0, 0.0])
system.actors.add(lbf)
This part of the script specifies the fluid that will get the system
moving. Here agrid \(=\Delta x\) is the spatial discretisation
step, tau is the time step that will be the same as the time step
for particles, viscosity visc and density dens of the fluid are
physical parameters scaled to lattice units. fric is a
(non-physical) friction parameter that enters the fluid-object
interaction and has to be set carefully. Finally, ext_force_density sets the
force-per-unit-volume vector that drives the fluid. Another option to
add momentum to fluid is by specifying the velocity on the boundaries.
Here we achieved the movement of the fluid by applying external force. Another alternative is to set up a wall/rhomboid with velocity. This does not mean that the physical boundary is moving, but rather that it transfers specified momentum onto the fluid.
16.5.2.3. Specification of boundaries¶
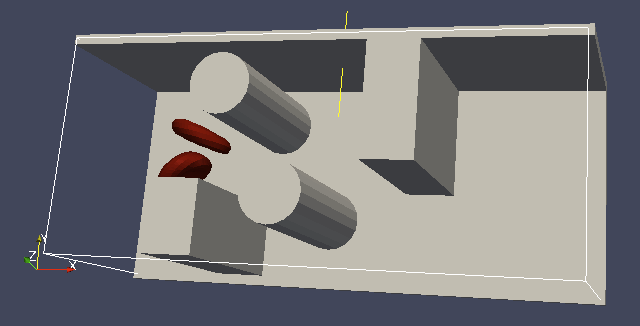
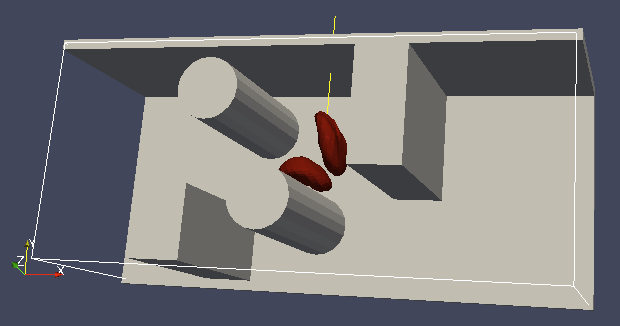
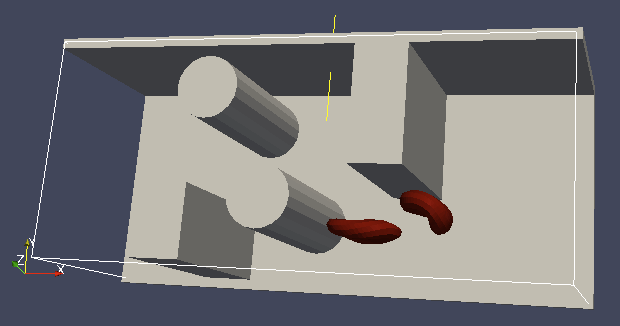
Each wall and obstacle has to be specified separately as a fluid boundary and as a particle constraint. The former enters the simulation as a boundary condition for the fluid, the latter serves for particle-boundary interactions. Sample cylinder and rhomboid can then be defined as follows. First we define the two shapes:
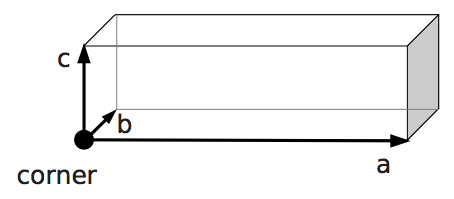
boundary1 = shapes.Rhomboid(corner=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
a=[boxX, 0.0, 0.0],
b=[0.0, boxY, 0.0],
c=[0.0, 0.0, 1.0],
direction=1)
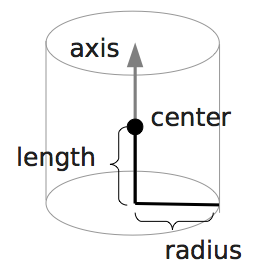
boundary2 = shapes.Cylinder(center=[11.0, 2.0, 7.0],
axis=[0.0, 0.0, 1.0],
length=7.0,
radius=2.0,
direction=1)
The direction=1 determines that the fluid is on the outside. Next
we create boundaries for the fluid:
system.lbboundaries.add(lbboundaries.LBBoundary(shape=boundary1))
system.lbboundaries.add(lbboundaries.LBBoundary(shape=boundary2))
Followed by constraints for cells:
system.constraints.add(shape=boundary1, particle_type=10)
system.constraints.add(shape=boundary2, particle_type=10)
The particle_type=10 will be important for specifying cell-wall
interactions later. And finally, we output the boundaries for
visualisation:
output_vtk_rhomboid(corner=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
a=[boxX, 0.0, 0.0],
b=[0.0, boxY, 0.0],
c=[0.0, 0.0, 1.0],
out_file="output/sim1/wallBack.vtk")
output_vtk_cylinder(center=[11.0, 2.0, 7.0],
axis=[0.0, 0.0, 1.0],
length=7.0,
radius=2.0,
n=20,
out_file="output/sim1/obstacle.vtk")
n.
This specifies number of rectangular faces on the side.16.5.2.4. Specification of interactions¶
Since we have two cells, we can also set up the cell-cell interactions so that they know about each other:
system.non_bonded_inter[0, 1].membrane_collision.set_params(
membrane_a=0.0001, membrane_n=1.2, membrane_cut=0.1,
membrane_offset=0.0)
These interactions act pointwise, e.g. each particle of type 0 (all
mesh points of cell0) has a repulsive membrane collision interaction
with each particle of type 1 (all mesh points of cell1) once the pair
gets closer than membrane_cut.
Similar interaction is defined with the boundaries:
system.non_bonded_inter[0, 10].soft_sphere.set_params(
soft_a=0.0001, soft_n=1.2, soft_cut=0.1, soft_offset=0.0)
These interactions are also pointwise, e.g. each particle of type 0
(that means all mesh points of cell) will have a repulsive soft-sphere
interaction with all boundaries of type 10 (here all boundaries) once it
gets closer than soft_cut. The parameters soft_a and soft_n
adjust how strong the interaction is and soft_offset is a distance
offset, which will always be zero for our purposes.
16.5.2.5. System integration¶
And finally, the heart of this script is the integration loop at the end:
for i in range(1, 101):
system.integrator.run(steps=500)
cell.output_vtk_pos_folded(filename="output/sim1/cell_"
+ str(i) + ".vtk")
print "time: ", str(i * time_step)
print "Simulation completed."
This simulation runs for 100 cycles. In each cycle, 500 integration
steps are performed and output is saved into files
output/sim1/cell_i.vtk. Note that they differ only by the number
before the .vtk extension (this variable changes due to the for
loop) and this will allow us to animate them in the visualisation
software. str changes the type of i from integer to string, so
that it can be used in the filename. The strings can be joined together
by the + sign. Also, in each pass of the loop, the simulation time is
printed in the terminal window and when the integration is complete, we
should get a message about it.
16.5.2.6. Running the simulation¶
The script can be executed in terminal using
../pypresso script.py
Here script.py is the name of the script we just went over and
../pypresso should be replaced with the path to your executable.
This command assumes that we are currently in the same directory as the
script. Once the command is executed, messages should appear on the
terminal about the creation of cell type, cell and the integration
steps.
16.5.2.7. Writing out data¶
In the script, we have used the commands such as
cell.output_vtk_pos_folded(filename="output/sim1/cell_" + str(i) + ".vtk")
to output the information about cell in every pass of the simulation loop. These files can then be used for inspection in ParaView and creation of animations. It is also possible to save a .vtk file for the fluid. And obviously, one can save various types of other data into text or data files for further processing and analysis.
16.5.3. Visualization in ParaView¶
16.5.3.1. File format¶
ParaView (download at http://www.paraview.org) accepts .vtk files. For our cells we use the following format:
# vtk DataFile Version 3.0
Data
ASCII
DATASET POLYDATA
POINTS 393 float
p0x p0y p0z
p1x p1y p1z
...
p391x p391y p391z
p392x p392y p392z
TRIANGLE_STRIPS num_triang 4*num_triang
3 p1 p2 p3
3 p1 p3 p5
...
3 p390 p391 p392
num_triang) and the each line/triangle is specified by 4 numbers
(so we are telling ParaView to expect 4 * num_triang numbers in
the following lines. Each line begins with 3 (which stands for a
triangle) and three point IDs that tell us which three points (from
the order above) form this specific triangle.16.5.3.2. Color coding of scalar data by surface points¶
It is possible to save (and visualize) data corresponding to individual surface points. These data can be scalar or vector values associated with all surface points. At the end of the .vtk file above, add the following lines:
POINT_DATA 393
SCALARS sample_scalars float 1
LOOKUP_TABLE default
value-at-p0
value-at-p1
...
value-at-p392
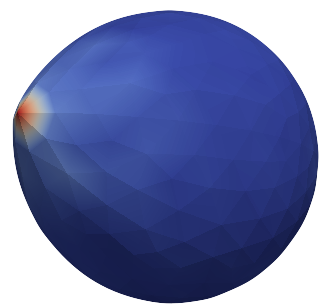
Stretched sphere after some relaxation, showing magnitude of total stretching force in each node.
16.5.3.3. Color coding of scalar data by triangles¶
It is also possible to save (and visualize) data corresponding to individual triangles
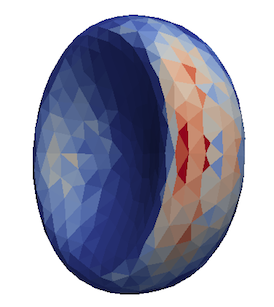
Red blood cell showing which triangles (local surface areas) are under most strain in shear flow.
In such case, the keyword POINT_DATA is changed to CELL_DATA and the number of
triangles is given instead of number of mesh points.
# vtk DataFile Version 3.0
Data
ASCII
DATASET POLYDATA
POINTS 4 float
1 1 1
3 1 1
1 3 1
1 1 3
TRIANGLE_STRIPS 3 12
3 0 1 2
3 0 2 3
3 0 1 3
CELL_DATA 3
SCALARS sample_scalars float 1
LOOKUP_TABLE default
0.0
0.5
1.0
16.5.3.4. Multiple scalar data in one .vtk file¶
If one wants to switch between several types of scalar values corresponding to mesh nodes, these are specifies consecutively in the .vtk file, as follows. Their names (scalars1 and scalars2 in the following example) appear in a drop-down menu in ParaView.
POINT_DATA 393
SCALARS scalars1 float 1
LOOKUP_TABLE default
value1-at-p0
value1-at-p1
...
value1-at-p392
SCALARS scalars2 float 1
LOOKUP_TABLE default
value2-at-p0
value2-at-p1
...
value2-at-p392
16.5.3.5. Vector data for objects .vtk file¶
POINT_DATA 393
VECTORS vector_field float
v1-at-p0 v2-at-p0 v3-at-p0
v1-at-p1 v2-at-p1 v3-at-p1
...
v1-at-p391 v2-at-p391 v3-at-p392
Example of vector data stored in points of the object
16.5.3.6. Automatic loading¶
paraview --script=loading-script.py and all the steps for creating
that scenario will be executed and you end up with the velocity field
visualized.16.5.4. Available Object-in-fluid (OIF) classes¶
keywords, parameter values, vectors16.5.4.1. class OifCellType¶
For those familiar with earlier version of object-in-fluid framework, this class corresponds to the oif_emplate in tcl. It contains a “recipe” for creating cells of the same type. These cells can then be placed at different locations with different orientation, but their elasticity and size is determined by the CellType. There are no actual particles created at this stage. Also, while the interactions are defined, no bonds are created here.
OifCellType.print_info()
OifCellType.mesh.output_mesh_triangles(filename)
nodesfile=nodes.dat - input file. Each line contains three
real numbers. These are the \(x, y, z\) coordinates of individual
surface mesh nodes of the objects centered at [0,0,0] and normalized
so that the “radius” of the object is 1.trianglesfile=triangles.dat - input file. Each line contains
three integers. These are the ID numbers of the mesh nodes as they
appear in nodes.dat. Note that the first node has ID 0.system=system Particles of cells created using this
template will be added to this system. Note that there can be only one
system per simulation.ks=value - elastic modulus for stretching forces.kslin= value - elastic modulus for linear stretching forces.kb= value - elastic modulus for bending forces.kal= value - elastic modulus for local area forces.ks, kb and kal set elastic parameters for
local interactions: ks for edge stiffness, kb for angle
preservation stiffness and kal for triangle area preservation
stiffness. Currently, the stiffness is implemented to be uniform over
the whole object, but with some tweaking, it is possible to have
non-uniform local interactions.ks) and linear stretching
(kslin) - these two options cannot be used simultaneously:kvisc=value - elastic modulus for viscosity of the membrane.
Viscosity slows down the reaction of the membrane.kag=value - elastic modulus for global area forceskv=value - elastic modulus for volume forcesresize=(x, y, z) - coefficients, by which the coordinates
stored in \(nodesfile\) will be stretched in the \(x, y, z\)
direction. The default value is (1.0, 1.0, 1.0).mirror=(x, y, z) - whether the respective coordinates should
be flipped around 0. Arguments \(x, y, z\) must be either 0 or 1.
The reflection of only one coordinate is allowed so at most one
argument is set to 1, others are 0. For example mirror=(0, 1, 0)
results in flipping the coordinates (x, y, z) to (x, -y, z). The
default value is (0, 0, 0).normal - by default set to \(False\), however without this
option enabled, the membrane collision (and thus cell-cell
interactions) will not work.check_orientation - by default set to \(True\). This options
performs a check, whether the supplied \(trianglesfile\) contains
triangles with correct orientation. If not, it corrects the
orientation and created cells with corrected triangles. It is useful
for new or unknown meshes, but not necessary for meshes that have
already been tried out. Since it can take a few minutes for larger
meshes (with thousands of nodes), it can be set to \(False\). In
that case, the check is skipped when creating the CellType and a
warning is displayed.CellType.mesh.OutputMeshTriangles(\(filename\)), so that the
check does not have to be used repeatedly.CellType.mesh.output_mesh_triangles(\(filename\)) - this is
useful after checking orientation, if any of the triangles where
corrected. This method saves the current triangles into a file that
can be used as input in the next simulations.CellType.print_info() - prints the information about the template.16.5.4.2. class OifCell¶
OifCell.set_origin([x, y, z])
OifCell.get_origin()
OifCell.get_origin_folded()
OifCell.get_approx_origin()
OifCell.get_approx_origin_folded()
OifCell.get_velocity()
OifCell.set_velocity([x, y, z])
OifCell.pos_bounds()
OifCell.surface()
OifCell.volume()
OifCell.get_diameter()
OifCell.get_n_nodes()
OifCell.set_force([x, y, z])
OifCell.kill_motion()
OifCell.unkill_motion()
OifCell.output_vtk_pos(filename.vtk)
OifCell.output_vtk_pos_folded(filename.vtk)
OifCell.append_point_data_to_vtk(filename.vtk, dataname, data, firstAppend)
OifCell.output_raw_data(filename, rawdata)
OifCell.output_mesh_nodes(filename)
OifCell.set_mesh_nodes(filename)
OifCell.elastic_forces(elasticforces, fmetric, vtkfile, rawdatafile)
OifCell.print_info()
cell_type - object will be created using nodes, triangle
incidences, elasticity parameters and initial stretching saved in this
cellType.part_type=type - must start at 0 for the first cell and
increase consecutively for different cells. Volume calculation of
individual objects and interactions between objects are set up using
these types.origin=(x, y, z) - center of the object will be at this
point.rotate=(x, y, z) - angles in radians, by which the object
will be rotated about the \(x, y, z\) axis. Default value is (0.0,
0.0, 0.0). Value (\(\pi/2, 0.0, 0.0\)) means that the object will
be rotated by \(\pi/2\) radians clockwise around the \(x\)
axis when looking in the positive direction of the axis.mass=m - mass of one particle. Default value is 1.0.OifCell.set_origin(o) - moves the object such that the origin
has coordinates o=(x, y, z).OifCell.get_origin() - outputs the location of the center of the
object.OifCell.get_origin_folded() - outputs the location of the center of
the object. For periodical movements the coordinates are folded
(always within the computational box).OifCell.get_approx_origin() - outputs the approximate location of
the center of the object. It is computed as average of 6 mesh points
that have extremal \(x, y\) and \(z\) coordinates at the time
of object loading.OifCell.get_approx_origin_folded() - outputs the approximate location
of the center of the object. It is computed as average of 6 mesh
points that have extremal \(x, y\) and \(z\) coordinates at
the time of object loading. For periodical movements the coordinates
are folded (always within the computational box). TODO: this is not
implemented yet, but it should beOifCell.get_velocity() - outputs the average velocity of the
object. Runs over all mesh points and outputs their average velocity.OifCell.set_velocity(v) - sets the velocities of all mesh
points to v=(\(v_x\), \(v_y\), \(v_z\)).OifCell.pos_bounds() - computes six extremal coordinates of the
object. More precisely, runs through the all mesh points and returns
the minimal and maximal \(x\)-coordinate, \(y\)-coordinate and
\(z\)-coordinate in the order (\(x_{max}\), \(x_{min}\),
\(y_{max}\), \(y_{min}\), \(z_{max}\), \(z_{min}\)).OifCell.surface() - outputs the surface of the object.OifCell.volume() - outputs the volume of the object.OifCell.get_diameter() - outputs the largest diameter of the
object.OifCell.get_n_nodes() - returns the number of mesh nodes.OifCell.set_force(f) - sets the external force vector
f=(\(f_x\), \(f_y\), \(f_z\)) to all mesh nodes of
the object. Setting is done using command p.set_force(f).
Note, that this command sets the external force in each integration
step. So if you want to use the external force only in one iteration,
you need to set zero external force in the following integration step.OifCell.kill_motion() - stops all the particles in the object
(analogue to the command p.kill_motion()).OifCell.unkill_motion() - enables the movement of all the particles
in the object (analogue to the command p.unkill_motion()).OifCell.output_vtk_pos(filename.vtk) - outputs the mesh of the
object to the desired filename.vtk. ParaView can directly visualize
this file.OifCell.output_vtk_pos_folded(filename.vtk) - outputs the mesh of
the object to the desired filename.vtk. ParaView can directly
visualize this file. For periodical movements the coordinates are
folded (always within the computational box).OifCell.append_point_data_to_vtk(filename.vtk, dataname,
data, firstAppend) - outputs the specified scalar data to an
existing \(filename.vtk\). This is useful for ParaView
visualisation of local velocity magnitudes, magnitudes of forces, etc.
in the meshnodes and can be shown in ParaView by selecting the
\(dataname\) in the \(Properties\) toolbar. It is possible to
consecutively write multiple datasets into one \(filename.vtk\).
For the first one, the \(firstAppend\) parameter is set to
\(True\), for the following datasets, it needs to be set to
\(False\). This is to ensure the proper structure of the output
file.OifCell.output_raw_data(filename, rawdata) - outputs the
vector rawdata about the object into the filename.OifCell.output_mesh_nodes(filename) - outputs the positions of
the mesh nodes to filename. In fact, this command creates a new
nodes.dat file that can be used by the method
OifCell.set_mesh_nodes(nodes.dat). The center of the object is
located at point (0.0, 0.0, 0.0). This command is aimed to store the
deformed shape in order to be loaded later.OifCell.set_mesh_nodes(filename) - deforms the object in such a
way that its origin stays unchanged, however the relative positions of
the mesh points are taken from file filename. The filename should
contain the coordinates of the mesh points with the origin location at
(0.0, 0.0, 0.0). The procedure also checks whether number of lines in
the filename is the same as the corresponding value from
OifCell.get_n_nodes().OifCell.elastic_forces(elasticforces, fmetric, vtkfile,
rawdatafile) - this method can be used in two different ways. One is
to compute the elastic forces locally for each mesh node and the other
is to compute the f-metric, which is an approximation of elastic
energy.OifCell.print_info() - prints the information about the elastic
object.16.5.4.3. Short utility procedures¶
get_n_triangle(\(\mathbf{a,b,c}\)) - returns the normal n
to the triangle given by points (a, b, c).norm(\(\mathbf{v}\)) - returns the norm of the vector v.distance(\(\mathbf{a,b}\)) - returns the distance between
points a and b.area_triangle(\(\mathbf{a,b,c}\)) - returns the area of the
given triangle (a, b, c).angle_btw_triangles(\(\mathbf{p}_1\), \(\mathbf{p}_2\),
\(\mathbf{p}_3\), \(\mathbf{p}_4\) - returns the angle
\(\phi\) between two triangles: (\(\mathbf{p}_1\),
\(\mathbf{p}_2\), \(\mathbf{p}_3\)) and (\(\mathbf{p}_3\),
\(\mathbf{p}_2\), \(\mathbf{p}_4\)) that have a common edge
(\(\mathbf{p}_2\), \(\mathbf{p}_3\)).discard_epsilon(\(x\)) - needed for rotation; discards very
small numbers x.oif_neo_hookean_nonlin(\(\lambda\)) - nonlinearity for neo-Hookean stretchingcalc_stretching_force(\(k_s,\ \mathbf{p}_A,\ \mathbf{p}_B,\ dist_0,\ dist\))
- computes the nonlinear stretching force with given \(k_s\) for
points \(\mathbf{p}_A\) and \(\mathbf{p}_B\) given by their
coordinates, whose initial distance was dist0 and current distance
is dist.calc_linear_stretching_force(\(k_s,\ \mathbf{p}_A,\ \mathbf{p}_B,\ dist_0,\ dist\))
- computes the linear stretching force with given \(k_s\) for
points \(\mathbf{p}_A\) and \(\mathbf{p}_B\) given by their
coordinates, whose initial distance was dist0 and current distance
is dist.calc_bending_force(\(k_b,\ \mathbf{p}_A,\ \mathbf{p}_B,\ \mathbf{p}_C,\ \mathbf{p}_D,\ \phi_0,\ \phi\))
- computes the bending force with given \(k_b\) for points
\(\mathbf{p}_A\), \(\mathbf{p}_B\), \(\mathbf{p}_C\) and
\(\mathbf{p}_D\) (\(\triangle_1\)=BAC;
\(\triangle_2\)=BCD) given by their coordinates; the initial
angle for these two triangles was \(\phi_0\), the current angle is
\(\phi\).calc_local_area_force(\(k_{al},\ \mathbf{p}_A,\ \mathbf{p}_B,\ \mathbf{p}_C,\ A_0,\ A\))
- computes the local area force with given \(k_{al}\) for points
\(\mathbf{p}_A\), \(\mathbf{p}_B\) and \(\mathbf{p}_C\)
given by their coordinates; the initial area of triangle ABC was
\(A_0\), the current area is \(A\).calc_global_area_force(\(k_{ag},\ \mathbf{p}_A,\ \mathbf{p}_B,\ \mathbf{p}_C,\ A_{g0},\ A_g\))
- computes the global area force with given \(k_{ag}\) for points
\(\mathbf{p}_A\), \(\mathbf{p}_B\) and \(\mathbf{p}_C\)
given by their coordinates; the initial surface area of the object was
\(A_{g0}\), the current surface area of the object is \(A_g\).calc_volume_force(\(k_v,\ \mathbf{p}_A,\ \mathbf{p}_B,\ \mathbf{p}_C,\ V_0\ V\))
- computes the volume force with given \(k_v\) for points
\(\mathbf{p}_A\), \(\mathbf{p}_B\) and \(\mathbf{p}_C\)
given by their coordinates; the initial volume of the object was
\(V_0\), the current volume of the object is \(V\).output_vtk_rhomboid(\(\mathbf{corner}, \mathbf{a}, \mathbf{b}, \mathbf{c}, outFile.vtk\))
- outputs rhomboid boundary for later visualisation in ParaView.output_vtk_cylinder(\(\mathbf{center}, \mathbf{normal}, L, r, n, outFile.vtk\))
- outputs cylinder boundary for later visualisation in ParaView.output_vtk_lines(\(lines, outFile.vtk\)) - outputs a set of
line segments for later visualisation in ParaView.16.5.4.4. Description of helper classes¶
Awareness of these classes is not necessary for a user of OIF module, but is essential for developers who wish to modify it because it shows how the object data are stored.
classes FixedPoint and PartPoint
Class PartPoint represents a particle. These particles are then used as building blocks for edges, angles, triangles and ultimately the whole object mesh. Since we use a two-step process to create the objects, it is necessary to distinguish between a FixedPoint and PartPoint. FixedPoint is a point used by template and does not correspond to particle. The FixedPoints of one OifCellType form a mesh that is centered around origin. Only after it is stretched and shifted to the object origin are the PartPoints of the given object created.
classes Edge, Angle, Triangle, ThreeNeighbors
These classes represent the building blocks of a mesh. They are used to compute the elastic interactions: Edge is for stretching, Angle for bending, Triangle for local and global area and volume and ThreeNeigbors for calculation of outward normal vector needed for cell-cell interaction.
class Mesh
This class holds all the information about the geometry of the object, including nodes, edges, angles, triangles and neighboring points. The mesh of OifCellType is copied every time a new object (i.e. OifCell) of this type is created. This saves computational time, since the data for elastic interactions of the given object do not need to be recalculated every time.
16.6. Electrokinetics¶
The electrokinetics setup in ESPResSo allows for the description of electro-hydrodynamic systems on the level of ion density distributions coupled to a Lattice Boltzmann (LB) fluid. The ion density distributions may also interact with explicit charged particles, which are interpolated on the LB grid. In the following paragraph we briefly explain the electrokinetic model implemented in ESPResSo, before we come to the description of the interface.
16.6.1. Electrokinetic Equations¶
In the electrokinetics code we solve the following system of coupled continuity, diffusion-advection, Poisson, and Navier-Stokes equations:
which define relations between the following observables
- \(n_k\)
- the number density of the particles of species \(k\),
- \(\vec{j}_k\)
- the number density flux of the particles of species \(k\),
- \(\Phi\)
- the electrostatic potential,
- \(\rho_{\mathrm{fl}}\)
- the mass density of the fluid,
- \(\vec{v}_{\mathrm{fl}}\)
- the advective velocity of the fluid,
and input parameters
- \(D_k\)
- the diffusion constant of species \(k\),
- \(\nu_k\)
- the mobility of species \(k\),
- \(q_k\)
- the charge of a single particle of species \(k\),
- \({l_\mathrm{B}}\)
- the Bjerrum length,
- \({k_\mathrm{B}T}\)
- the thermal energy given by the product of Boltzmann’s constant \(k_\text{B}\)and the temperature \(T\),
- \(\eta\)
- the dynamic viscosity of the fluid,
- \(\eta_{\text{b}}\)
- the bulk viscosity of the fluid.
The temperature \(T\), and diffusion constants \(D_k\) and mobilities \(\nu_k\) of individual species are linked through the Einstein-Smoluchowski relation \(D_k / \nu_k = {k_\mathrm{B}T}\). This system of equations combining diffusion-advection, electrostatics, and hydrodynamics is conventionally referred to as the Electrokinetic Equations.
The electrokinetic equations have the following properties:
On the coarse time and length scale of the model, the dynamics of the particle species can be described in terms of smooth density distributions and potentials as opposed to the microscale where highly localized densities cause singularities in the potential.
In most situations, this restricts the application of the model to species of monovalent ions, since ions of higher valency typically show strong condensation and correlation effects – the localization of individual ions in local potential minima and the subsequent correlated motion with the charges causing this minima.
Only the entropy of an ideal gas and electrostatic interactions are accounted for. In particular, there is no excluded volume.
This restricts the application of the model to monovalent ions and moderate charge densities. At higher valencies or densities, overcharging and layering effects can occur, which lead to non-monotonic charge densities and potentials, that can not be covered by a mean-field model such as Poisson–Boltzmann or this one.
Even in salt free systems containing only counter ions, the counter-ion densities close to highly charged objects can be overestimated when neglecting excluded volume effects. Decades of the application of Poisson–Boltzmann theory to systems of electrolytic solutions, however, show that those conditions are fulfilled for monovalent salt ions (such as sodium chloride or potassium chloride) at experimentally realizable concentrations.
Electrodynamic and magnetic effects play no role. Electrolytic solutions fulfill those conditions as long as they don’t contain magnetic particles.
The diffusion coefficient is a scalar, which means there can not be any cross-diffusion. Additionally, the diffusive behavior has been deduced using a formalism relying on the notion of a local equilibrium. The resulting diffusion equation, however, is known to be valid also far from equilibrium.
The temperature is constant throughout the system.
The density fluxes instantaneously relax to their local equilibrium values. Obviously one can not extract information about processes on length and time scales not covered by the model, such as dielectric spectra at frequencies, high enough that they correspond to times faster than the diffusive time scales of the charged species.
16.6.2. Setup¶
16.6.2.1. Initialization¶
import espressomd
sys = espressomd.System(box_l=[10.0, 10.0, 10.0])
sys.time_step = 0.0
sys.cell_system.skin = 0.4
ek = espressomd.electrokinetics.Electrokinetics(agrid=1.0, lb_density=1.0,
viscosity=1.0, friction=1.0, T=1.0, prefactor=1.0,
stencil='linkcentered', advection=True, fluid_coupling='friction')
sys.actors.add(ek)
Note
Features ELECTROKINETICS and LB_GPU required
The above is a minimal example how to initialize the LB fluid, and it is very similar to the lattice Boltzmann command in set-up. We therefore refer the reader to Chapter Lattice Boltzmann for details on the implementation of LB in ESPResSo and describe only the major differences here.
The first major difference with the LB implementation is that the electrokinetics set-up is a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) only implementation. There is no Central Processing Unit (CPU) version, and at this time there are no plans to make a CPU version available in the future. To use the electrokinetics features it is therefore imperative that your computer contains a CUDA capable GPU which is sufficiently modern.
To set up a proper LB fluid using this command one has to specify at
least the following options: agrid, lb_density, viscosity, friction, T, and prefactor. The other options can be
used to modify the behavior of the LB fluid. Note that the command does
not allow the user to set the time step parameter as is the case for the
lattice Boltzmann command, this parameter is instead taken directly from the value set for
espressomd.system.System.time_step. The LB mass density is set independently from the
electrokinetic number densities, since the LB fluid serves only as a
medium through which hydrodynamic interactions are propagated, as will
be explained further in the next paragraph. If no lb_density is specified, then our
algorithm assumes lb_density= 1.0. The two ‘new’ parameters are the temperature T at
which the diffusive species are simulated and the prefactor
associated with the electrostatic properties of the medium. See the
above description of the electrokinetic equations for an explanation of
the introduction of a temperature, which does not come in directly via a
thermostat that produces thermal fluctuations.
advection can be set to True or False. It controls whether there should be an
advective contribution to the diffusive species’ fluxes. Default is
True.
fluid_coupling can be set to "friction" or "estatics". This option determines the force
term acting on the fluid. The former specifies the force term to be the
sum of the species fluxes divided by their respective mobilities while
the latter simply uses the electrostatic force density acting on all
species. Note that this switching is only possible for the linkcentered
stencil. For all other stencils, this choice is hardcoded. The default
is "friction".
The feature EK_ELECTROSTATIC_COUPLING enables the action of the electrostatic potential due to the
electrokinetics species and charged boundaries on the MD particles. The
forces on the particles are calculated by interpolation from the
electric field which is in turn calculated from the potential via finite
differences. This only includes interactions between the species and
boundaries and MD particles, not between MD particles and MD particles.
To get complete electrostatic interactions a particles Coulomb method
like Ewald or P3M has to be activated too.
16.6.2.2. Diffusive Species¶
species = electrokinetics.Species(density=density, D=D, valency=valency,
ext_force_density=ext_force)
espressomd.electrokinetics.Species is used to initialize a diffusive species. Here the
options specify: the number density density, the diffusion coefficient D, the
valency of the particles of that species valency, and an optional external
(electric) force which is applied to the diffusive species. As mentioned
before, the LB density is completely decoupled from the electrokinetic
densities. This has the advantage that greater freedom can be achieved
in matching the internal parameters to an experimental system. Moreover,
it is possible to choose parameters for which the LB is more stable. The species has to be added to a LB fluid:
ek.add_species(species)
The LB fluid must be set up before using
espressomd.electrokinetics.Electrokinetics as shown above, before a
diffusive species can be added. The variables density, D, and
valency must be set to properly initialize the diffusive species; the
ext_force_density is optional.
16.6.2.3. Boundaries¶
ek_boundary = espressomd.electrokinetics.EKBoundary(charge_density=1.0, shape=my_shape)
system.ekboundaries.add(ek_boundary)
Note
Feature EK_BOUNDARIES required
The EKBoundary command allows one to set up (internal or external) boundaries for
the electrokinetics algorithm in much the same way as the command is
used for the LB fluid. The major difference with the LB command is given
by the option charge_density, with which a boundary can be endowed with a volume
charge density. To create a surface charge density, a combination of two
oppositely charged boundaries, one inside the other, can be used.
However, care should be taken to maintain the surface charge density when the value of agrid
is changed. Examples for possible shapes are wall, sphere, ellipsoid, cylinder,
rhomboid and hollowcone. We refer to the documentation of the
espressomd.shapes module for more possible shapes and information on
the options associated to these shapes. In order to properly set up the
boundaries, the charge_density and shape
must be specified.
16.6.3. Output¶
16.6.3.1. Fields¶
ek.print_vtk_boundary(path)
ek.print_vtk_density(path)
ek.print_vtk_velocity(path)
ek.print_vtk_potential(path)
A property of the fluid field can be exported into a
file in one go. Currently supported
are: density, velocity, potential and boundary, which give the LB fluid density, the LB fluid velocity,
the electrostatic potential, and the location and type of the
boundaries, respectively. The boundaries can only be printed when the
EK_BOUNDARIES is compiled in. The output is a vtk-file, which is readable by
visualization software such as ParaView [5] and Mayavi2 [6].
species.print_vtk_flux(path)
species.print_vtk_density(path)
These commands are similar to the above. They enable the export of diffusive species properties, namely: density and flux, which specify the number density and flux of species species, respectively.
16.6.3.2. Local Quantities¶
ek[0, 0, 0].velocity
ek[0, 0, 0].potential
ek[0, 0, 0].pressure
A single node can be addressed using three integer values
which run from 0 to dim_x/agrid, dim_y/agrid, and dim_z/agrid, respectively. The
velocity, electrostatic potential and the pressure of a LB fluid node can be obtained this way.
The local density and flux of a species can be obtained in the same fashion:
species[0, 0, 0].density
species[0, 0, 0].flux
| [5] | http://www.paraview.org/ |
| [6] | http://code.enthought.com/projects/mayavi/ |
16.7. Particle polarizability with thermalized cold Drude oscillators¶
Note
Requires features THOLE, P3M, LANGEVIN_PER_PARTICLE.
Note
Drude is only available for the P3M electrostatics solver and the Langevin thermostat.
Thermalized cold Drude oscillators can be used to simulate polarizable particles. The basic idea is to add a ‘charge-on-a-spring’ (Drude charge) to a particle (Drude core) that mimics an electron cloud which can be elongated to create a dynamically inducible dipole. The energetic minimum of the Drude charge can be obtained self-consistently, which requires several iterations of the system’s electrostatics and is usually considered computational expensive. However, with thermalized cold Drude oscillators, the distance between Drude charge and core is coupled to a thermostat so that it fluctuates around the SCF solution. This thermostat is kept at a low temperature compared to the global temperature to minimize the heat flow into the system. A second thermostat is applied on the centre of mass of the Drude charge + core system to maintain the global temperature. The downside of this approach is that usually a smaller time step has to be used to resolve the high frequency oscillations of the spring to get a stable system.
In ESPResSo, the basic ingredients to simulate such a system are split into three bonds:
- A Harmonic bond to account for the spring.
- A Thermalized distance bond with a cold thermostat on the Drude-Core distance.
- A Subtract P3M short-range bond to cancel the electrostatic interaction between Drude and core particles.
The system-wide thermostat has to be applied to the centre of mass and not to
the core particle directly. Therefore, the particles have to be excluded from
global thermostatting. With LANGEVIN_PER_PARTICLE enabled, we set the
temperature and friction coefficient of the Drude complex to zero, which allows
to still use a global Langevin thermostat for non-polarizable particles.
As the Drude charge should not alter the charge or mass of the Drude complex, both properties have to be subtracted from the core when adding the Drude particle. In the following convention, we assume that the Drude charge is always negative. It is calculated via the spring constant \(k\) and polarizability \(\alpha\) (in units of inverse volume) with \(q_d = -\sqrt{k \cdot \alpha}\).
The following helper method takes into account all the preceding considerations and can be used to conveniently add a Drude particle to a given core particle. As it also adds the first two bonds between Drude and core, these bonds have to be created beforehand:
from drude_functions import *
add_drude_particle_to_core(<system>, <harmonic_bond>, <thermalized_bond>,
<core particle>, <id drude>, <type drude>, <alpha>, <mass drude>,
<coulomb_prefactor>, <thole damping>, <verbose>)
- The arguments of the helper function are:
<system>: Theespressomd.System().<harmonic_bond>: The harmonic bond of the charge-on-a-spring. This is added between core and newly generated Drude particle<thermalized_bond>: The thermalized distance bond for the cold and hot thermostats.<core particle>: The core particle on which the Drude particle is added.<id drude>: The user-defined id of the Drude particle that is created.<type drude>: The user-defined type of the Drude particle. Each Drude particle of each complex should have an individual type (e.g. in an ionic system with Anions (type 0) and Cations (type 1), two new, individual Drude types have to be assigned).<alpha>: The polarizability volume.<coulomb_prefactor>: The Coulomb prefactor of the system. Used to calculate the Drude charge from the polarizability and the spring constant of the Drude bond.<thole damping>: (optional) An individual Thole damping parameter for the core-Drude pair. Only relevant if Thole damping is used (defaults to 2.6).<verbose>: (bool, optional) Prints out information about the added Drude particles (default: False)
What is still missing is the short-range exclusion bond between all Drude-core pairs. One bond type of this kind is needed per Drude type. The above helper function also tracks particle types, ids and charges of Drude and core particles, so a simple call of another helper function:
drude_helpers.setup_and_add_drude_exclusion_bonds(S)
will use this data to create a Subtract P3M short-range bond per Drude type
and set it up it between all Drude and core particles collected in calls of add_drude_particle_to_core().
16.7.1. Canceling intramolecular electrostatics¶
Note that for polarizable molecules (i.e. connected particles, coarse grained models etc.) with partial charges on the molecule sites, the Drude charges will have electrostatic interaction with other cores of the molecule. Often, this is unwanted, as it might be already part of the force-field (via. partial charges or parametrization of the covalent bonds). Without any further measures, the elongation of the Drude particles will be greatly affected be the close-by partial charges of the molecule. To prevent this, one has to cancel the interaction of the Drude charge with the partial charges of the cores within the molecule. This can be done with special bonds that subtracts the P3M short-range interaction of the charge portion \(q_d q_{partial}\). This ensures that only the dipolar interaction inside the molecule remains. It should be considered that the error of this approximation increases with the share of the long-range part of the electrostatic interaction. Two helper methods assist with setting up this exclusion. If used, they have to be called after all Drude particles are added to the system:
setup_intramol_exclusion_bonds(<system>, <molecule drude types>,
<molecule core types>, <molecule core partial charges>, <verbose>)
This function creates the requires number of bonds which are later added to the particles. It has to be called only once. In a molecule with \(N\) polarizable sites, \(N \cdot (N-1)\) bond types are needed to cover all the combinations. Parameters are:
<system>: Theespressomd.System().<molecule drude types>: List of the Drude types within the molecule.<molecule core types>: List of the core types within the molecule that have partial charges.<molecule core partial charges>: List of the partial charges on the cores.<verbose>: (bool, optional) Prints out information about the created bonds (default: False)
After setting up the bonds, one has to add them to each molecule with the following method:
add_intramol_exclusion_bonds(<system>, <drude ids>, <core ids>, <verbose>)
This method has to be called for all molecules and needs the following parameters:
<system>: Theespressomd.System().<drude ids>: The ids of the Drude particles within one molecule.<core ids>: The ids of the core particles within one molecule.<verbose>: (bool, optional) Prints out information about the added bonds (default:False)
Internally, this is done with the bond described in Subtract P3M short-range bond, that simply adds the p3m shortrange pair-force of scale \(- q_d q_{partial}\) the to bonded particles.
See also
Often used in conjunction with Drude oscillators is the Thole correction to damp dipole-dipole interactions on short distances. It is available in ESPResSo as a non-bonded interaction.
16.8. Reaction Ensemble¶
Note
The whole Reaction Ensemble module uses Monte Carlo moves which require potential energies. Therefore the Reaction Ensemble requires support for energy calculations for all interactions which are used in the simulation.
For a description of the available methods see espressomd.reaction_ensemble.
An Example script can be found here:
The reaction ensemble [ST94][HTBL+08] allows to simulate chemical reactions which can be represented by the general equation:
where \(\nu_i\) is the stoichiometric coefficient of species \(S_i\). By convention, stoichiometric coefficients of the species on the left-hand side of the reaction (reactants) attain negative values, and those on the right-hand side (products) attain positive values, so that the reaction can be equivalently written as
The equilibrium constant of the reaction is then given as
Here \(k_B\) is the Boltzmann constant, \(T\) is temperature, \(\Delta_{\mathrm{r}}G^{\ominus}\) standard Gibbs free energy change of the reaction, and \(\mu_i^{\ominus}\) the standard chemical potential (per particle) of species \(i\). Note that thermodynamic equilibrium is independent of the direction in which we write the reaction. If it is written with left and right-hand side swapped, both \(\Delta_{\mathrm{r}}G^{\ominus}\) and the stoichiometric coefficients attain opposite signs, and the equilibrium constant attains the inverse value. Further, note that the equilibrium constant \(K\) is the dimensionless thermodynamic, concentration-based equilibrium constant, defined as
where \(\bar\nu=\sum_i \nu_i\), and \(c^{\ominus}\) is the reference concentration, at which the standard chemical potential \(\Delta_{\mathrm{r}}G^{\ominus}\) was determined. In practice, this constant is often used with the dimension of \((c^{\ominus})^{\bar\nu}\)
A simulation in
the reaction ensemble consists of two types of moves: the reaction move
and the configuration move. The configuration move changes the configuration
of the system. It is not performed by the Reaction Ensemble module, and can be
performed by a suitable molecular dynamics or a Monte Carlo scheme. The
reactant_ensemble command takes care only of the reaction moves.
In the forward reaction, the appropriate number of reactants (given by
\(\nu_i\)) is removed from the system, and the concomitant number of
products is inserted into the system. In the backward reaction,
reactants and products exchange their roles. The acceptance probability
\(P^{\xi}\) for move from state \(o\) to \(n\) reaction
ensemble is given by the criterion [ST94]
where \(\Delta E=E_\mathrm{new}-E_\mathrm{old}\) is the change in potential energy, \(V\) is the simulation box volume, and \(\beta=1/k_\mathrm{B}T\). The extent of reaction, \(\xi=1\) for the forward, and \(\xi=-1\) for the backward direction. The parameter \(\Gamma\) proportional to the reaction constant. It is defined as
where \(\left<N_i\right>/V\) is the average number density of particles of type \(i\). Note that the dimension of \(\Gamma\) is \(V^{\bar\nu}\), therefore its units must be consistent with the units in which Espresso measures the box volume, i.e. \(\sigma^3\).
It is often convenient, and in some cases even necessary, that some particles representing reactants are not removed from or placed at randomly in the system but their identity is changed to that of the products, or vice versa in the backward direction. A typical example is the ionization reaction of weak polyelectrolytes, where the ionizable groups on the polymer have to remain on the polymer chain after the reaction. The replacement rule is that the identity of a given reactant type is changed to the corresponding product type as long as the corresponding coefficients allow for it. Corresponding means having the same position (index) in the python lists of reactants and products which are used to set up the reaction.
16.8.1. Converting tabulated reaction constants to internal units in Espresso¶
The implementation in Espresso requires that the dimension of \(\Gamma\) is consistent with the internal unit of volume, \(\sigma^3\). The tabulated values of equilibrium constants for reactions in solution, \(K_c\), typically use \(c^{\ominus} = 1\,\mathrm{moldm^{-3}}\) as the reference concentration, and have the dimension of \((c^{\ominus})^{\bar\nu}\). To be used with Espresso, the value of \(K_c\) has to be converted as
where \(N_{\mathrm{A}}\) is the Avogadro number. For gas-phase reactions, the pressure-based reaction constant, \(K_p\) is often used, which can be converted to \(K_c\) as
where \(p^{\ominus}=1\,\mathrm{atm}\) is the standard pressure.
16.8.2. Wang-Landau Reaction Ensemble¶
An Example script can be found here:
Combination of the Reaction Ensemble with the Wang-Landau algorithm
[WL01]
allows for enhanced sampling of the reacting system, and
and for the determination of the density of states with respect
to the reaction coordinate or with respect to some other collective
variable [LHS17b]. Here the 1/t Wang-Landau
algorithm [BP07] is implemented since it
does not suffer from systematic errors. Additionally to the above
commands for the reaction ensemble use the following commands for the
Wang-Landau reaction ensemble. For a description of the available methods see espressomd.reaction_ensemble:
16.8.3. Constant pH simulation using the Reaction Ensemble¶
An Example script can be found here:
In the constant pH method due to Reed and Reed [RR92] it is possible to set the chemical potential of \(H^{+}\) ions, assuming that the simulated system is coupled to an infinite reservoir. This value is the used to simulate dissociation equilibrium of acids and bases. Under certain conditions, the constant pH method can yield equivalent results as the reaction ensemble [LHS17a]. However, it treats the chemical potential of \(H^{+}\) ions and their actual number in the simulation box as independent variables, which can lead to serious artifacts. The constant pH method can be used within the reaction ensemble module by initializing the reactions with the standard commands of the reaction ensemble.
The dissociation constant, which is the input of the constant pH method, is the equilibrium constant \(K_c\) for the following reaction:
For an example of how to setup
a Constant pH simulation, see the file in the testsuite directory.
For a description of the available methods see espressomd.reaction_ensemble:
16.8.4. Grand canonical ensemble simulation using the Reaction Ensemble¶
As a special case, all stoichiometric coefficients on one side of the chemical reaction can be set to zero. Such reaction creates particles ex nihilo, and is equivalent to exchange with a reservoir. Then the simulation in the reaction ensemble becomes equivalent with the grandcanonical simulation. Formally, this can be expressed by the reaction
where, if \(\nu_A=1\), the reaction constant \(\Gamma\) defines the chemical potential of species A. However, if \(\nu_A\neq 1\), the statistics of the reaction ensemble becomes equivalent to the grandcanonical only in the limit of large average number of species A in the box. If the reaction contains more than one product, then the reaction constant \(\Gamma\) defines only the sum of their chemical potentials but not the chemical potential of each product alone.
Since the Reaction Ensemble acceptance transition probability can be derived from the grand canonical acceptance transition probability we can use the reaction ensemble to implement grand canonical simulation moves. This is done via adding reactions that only have reactants (for the deletion of particles) or only have products (for the creation of particles). There exists a one to one mapping of the expressions in the grand canonical transition probabilities and the expressions in the reaction ensemble transition probabilities.
16.8.5. Widom Insertion (for homogeneous systems)¶
An example script can be found here: